ACL Injuries: Why They are Increasing & How to Avoid Them

Athlete suffering ACL injury during sudden knee twist.
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament injuries are probably among the highly rising ones, particularly in athletes and active individuals. The ACL is one of the major ligaments of the knee, which basically holds the knee stable for us to run, jump and change direction in a comfortable way. Upon tearing, it would be associated with marked pain, swelling and long-term knee instability. Understanding why ACL injuries are on the rise and how to prevent them is important to anyone who lives an active lifestyle.
What is an ACL Injury?
The ACL is one of the four main ligaments of the knee. It connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone) and limits the forward motion of the tibia relative to the femur. An injury to the ACL usually consists of either an overstretch or a complete tear in the ligament.
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden severe knee pain
- Swelling within hours of injury
- Feeling of instability or the knee “giving way”
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight
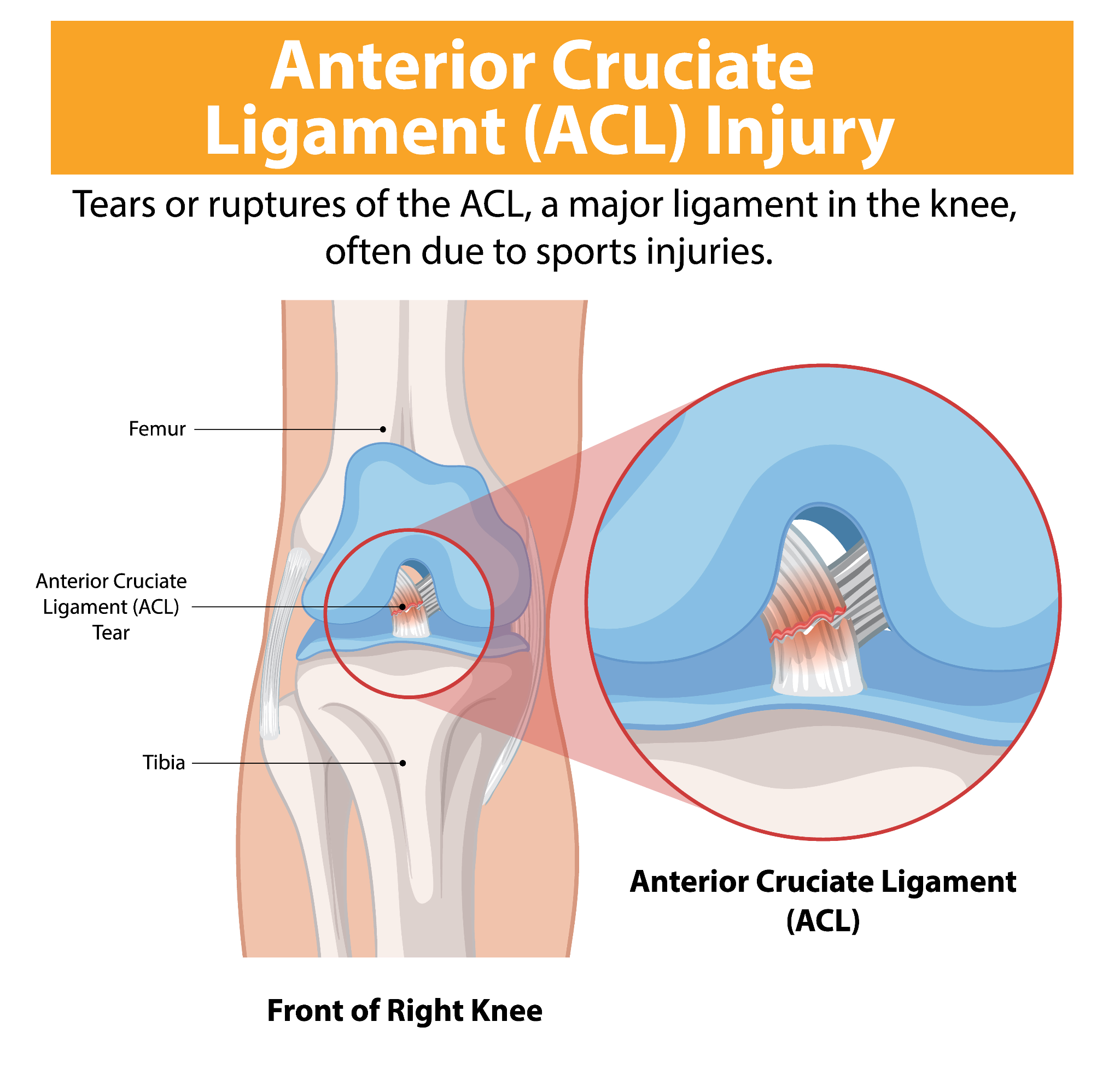
Medical infographic explaining ACL tear in the knee joint.
Why Are ACL Injuries on the Rise?
Injuries to the ACL have increased noticeably in recent years, especially in young athletes and among women. These are due to several reasons:
1. Increased Sports Participation
More people are now participating in high-intensity sports such as football, basketball and soccer, at increasingly younger ages and without proper training in how to move effectively.
2. Early Specialization in Sport
Concentrating on one sport all year increases children's and teenagers' risks for overuse injuries including ACL tears due to repetitive stress on the knees.
3. Higher Intensity Training
Competitive sports today require more agility, speed and strength, placing additional stress on the ACL.
4. Biomechanical Differences
Current studies indicate that anatomical and hormonal factors such as wider hips, small size of the ACL and fluctuating hormones affecting ligament laxity, predispose women to ACL injuries 2-8 times more often compared to men.
5. Improper Footwear & Playing Surfaces
Inadequate support from shoes or uneven playing surfaces can be a contributing factor to developing knee injuries.
Risk Factors for ACL Injuries
Some factors heighten the chances of an ACL tear:
- Previous knee injuries: A history of a previous ACL injury is one of the factors that heighten the chances of subsequent injury.
- Poor muscle strength: Specifically weak quadriceps and hamstrings. Poor technique includes incorrect landing, pivoting, or twisting movements.
- Sudden changes in direction: Quick stops or changes of direction during sports.
- Age and gender: The risk is greater for adolescents and young adults, especially females.
How to Prevent ACL Injuries
Athletes, above all, should focus on prevention. The following recommendations can help considerably to reduce the risk:
1. Make Your Muscles Stronger
Emphasize the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes and core muscles. Squats, lunges and hamstring curls are types of exercises that enhance knee stability.
2. Improve Flexibility & Balance
Stretching regularly prevents stiffness in the muscles that surround the knee. Balance exercises such as single-leg stands or using a wobble board may improve stability around the joints.
3. Learn Proper Movement Techniques
Rather, proper landing, pivoting and cutting can reduce knee strains. Coaches and physiotherapists can provide training drills for safe movement patterns.
4. Use of Protective Gear & Footwear
Supportive shoes suited for the sport lower the risk of injury. Knee braces may benefit people with a history of the ACL.
5. Avoid Overtraining
Include rest days and avoid repetitive actions that involve one sport only. Cross-training in different sports will minimize repetitive stress on the knees.
6. Neuromuscular Training Programs
Specific programs emphasise plyometric exercises, balance and agility drills.
Such exercises train the brain and muscles to coordinate better while going through any risky moves.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect an ACL injury, iImmediate medical care is necessary. Various imaging tests, including MRI, may be prescribed for confirmation of diagnosis by an orthopedic surgeon.
Early intervention can prevent further damage to the knee, such as meniscus tears or cartilage injury.

Orthopedic doctor examining knee of patient with ACL injury.
Treatment Options
Treatment based on injury severity, age and activity level:
1. Non-Surgical
For partial tears or less active individuals. Physical therapy emphasizes the strengthening and restoration of knee stability.
2. Surgical
ACL reconstruction with a graft taken from the patient's own tissue or from a donor. Followed by months of rehabilitation to regain strength and function.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after treatment is important:
Phase 1: Reduce swelling, regain motion
Phase 2: Strengthening muscles around the knee
Phase 3: Functional exercises for sport-specific movements
Phase 4: Gradual return to full activity or sports.
Most patients are able to return to pre-injury activity levels with appropriate adherence to rehab programs.
Expert ACL Care at Dr. Ankur Singh’s Clinic, Noida
Patients with ACL injuries receive advanced orthopedic treatment at Dr. Ankur Singh’s Clinic, Noida.
Dr. Ankur Singh is an internationally trained orthopedic surgeon committed to evidence-based treatment and patient-centric care.
At the clinic one will be able to:
- Diagnosis using advanced medical equipment.
- Personalised treatment plans encompassing both surgical and non-surgical options.
- Comprehensive rehabilitation programs, ensuring one's safety during recovery.
- Guidance on injury prevention and performance optimization in athletes.
Dr. Ankur Clinic is trusted by patients for professional care, smooth recovery and strategies to minimize future knee injuries.
Final Thoughts
While ACL injuries may be increasing, they can be greatly prevented through proper training and awareness. One must give great attention to strength, flexibility and proper techniques to protect the knees, especially among athletes who are specifically young women. Prompt diagnosis, coupled with proper rehabilitation, is important if an injury occurs.
Remember that your knees are the basis of your mobility. Protect them with smart training, good care and professional guidance at clinics like Dr. Ankur Singh’s Clinic, Noida.