Arthritis Pain Management: Non-Surgical and Surgical Options

Senior man walking outdoors as part of arthritis pain management
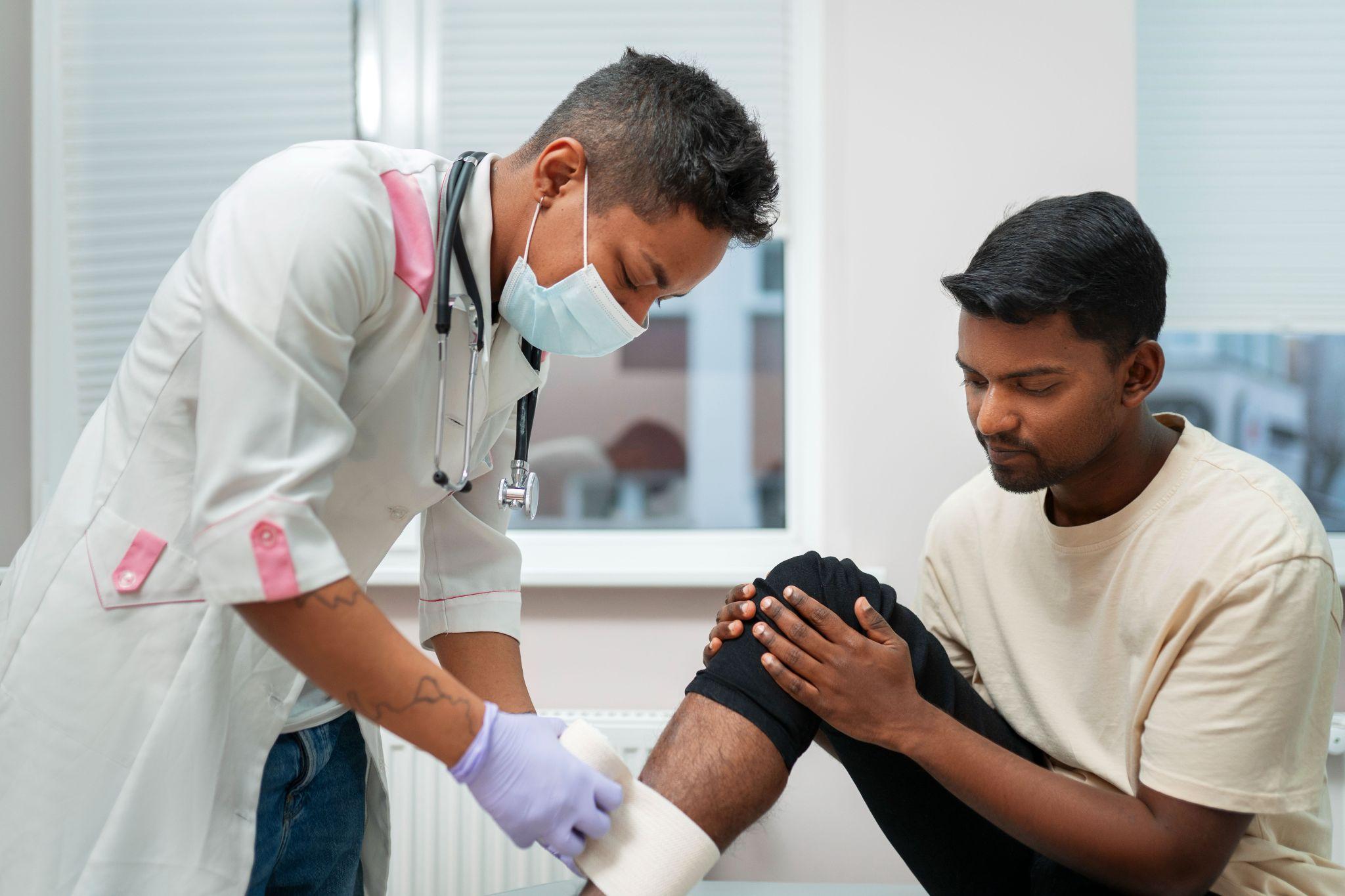
Arthritis ranks among the chief culprits behind enduring pain, stiffness, and immobility in joints. It is not age-specific, but the factors like age, overweight, past injuries concerning joints, and heredity increase one's vulnerability to it. The treatment techniques for arthritis pain are mainly aimed at avoiding the discomfort, enhancing the functioning of the affected joint, and keeping up the quality of life. Nowadays, if the condition is not very severe, patients can choose non-surgical treatments or undergo advanced surgical solutions.
This guide elaborates on the options for arthritis pain relief and thus assists patients in determining when conservative treatment is enough and when surgery for arthritis may become necessary.
Understanding Arthritis and Joint Pain
Arthritis is a pathological state characterized by inflamed and degenerated joints. The leading forms of arthritis are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. Of these, knee arthritis is particularly widespread because of the stress applied by body weight.
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
- Persistent joint pain
- Morning stiffness
- Swelling around joints
- Reduced range of motion
- Difficulty walking or performing daily activities
Diagnosis of the problem before it gets out of hand plays a key role in long-term joint pain management.
Non-Surgical Options for Arthritis Pain Relief
Non-surgical treatment is usually the first line of care for mild to moderate arthritis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes in day-to-day habits can significantly reduce arthritis pain:
- Weight management to minimise load on joint
- Low-impact exercises such as walking and swimming
- Proper posture
Losing weight alone can transform knee arthritis treatment outcomes.
Medications and Pain Control
Medications help manage inflammation and pain but do not reverse joint damage:
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Topical gels and creams
- Short-term medication during flare-ups
These should always be taken under orthopedic care to avoid side effects.

Medicines and pain relief tablets used in arthritis treatment
Physiotherapy and Joint Strengthening
Physiotherapy helps with joint stability and mobility:
- Strengthens surrounding muscles
- Improves balance and flexibility
- Reduces stiffness and pain
Structured physiotherapy is crucial for joint pain management.
Injection Therapies
Injections are often recommended when pain continues even after taking medication:
- Corticosteroid injections for inflammation
- Viscosupplementation to lubricate joints
These treatments can provide temporary but meaningful arthritis pain relief.
When Is Surgery Considered for Arthritis?
Arthritis surgery is taken into account when non-surgical options fail to provide relief and daily activities become hectic to do.
Indicators for Surgical Intervention
- Severe pain despite treatment
- Advanced joint damage on imaging
- Limited mobility affecting quality of life
Surgical decisions depend on age, activity level, and overall health.
Surgical Options for Arthritis Treatment
Arthroscopic Surgery
This procedure is suitable for the selected cases:
- Removes damaged cartilage fragments
- Reduces inflammation
It is not recommended for advanced arthritis but may help in early stages.
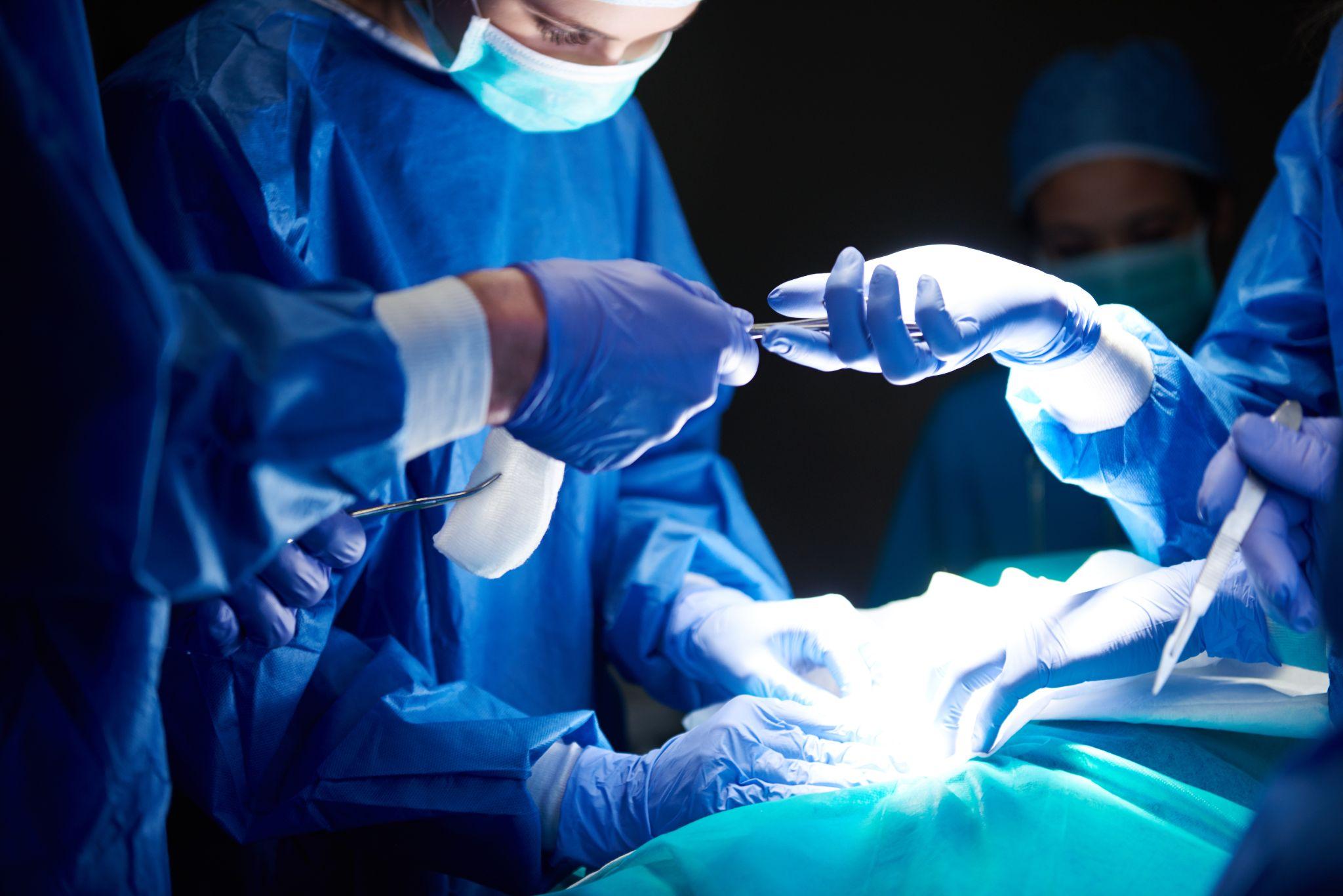
Orthopedic surgeons performing joint replacement surgery
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement is the most effective solution for end-stage arthritis:
- Knee replacement surgery restores mobility
- Damaged joint surfaces are replaced with artificial implants
- Long-term pain relief and functional improvement
Advancements in orthopedic care have made joint replacement safer and more durable.
Post-Surgical Recovery and Rehabilitation
A gradual recovery plays a crucial role in surgical success:
- Early mobilization
- Guided physiotherapy
- Gradual return to daily activities
Most patients experience significant improvement in pain and mobility within months.
Choosing the Right Arthritis Treatment Plan
Every single patient has their own individual characteristics. The effective management of arthritis pain has to depend on:
- Correct diagnosis
- Personalized treatment plan
- Monitoring on a regular basis
Visiting an orthopedic doctor with experience will guarantee the correct distribution between taking care of the patient in conservative ways and surgery.
For thorough arthritis treatment, correct diagnosis, and modern options for knee arthritis treatment, Dr. Ankur Singh, an orthopedic specialist trusted for his individualized approach to joint pain management and surgical expertise, is the one to consult.